Hybridized Finite Difference Scheme for Burgers' Equation
An introductory code base designed to teach the hybridization of non-dissipative central schemes with shock capturing schemes
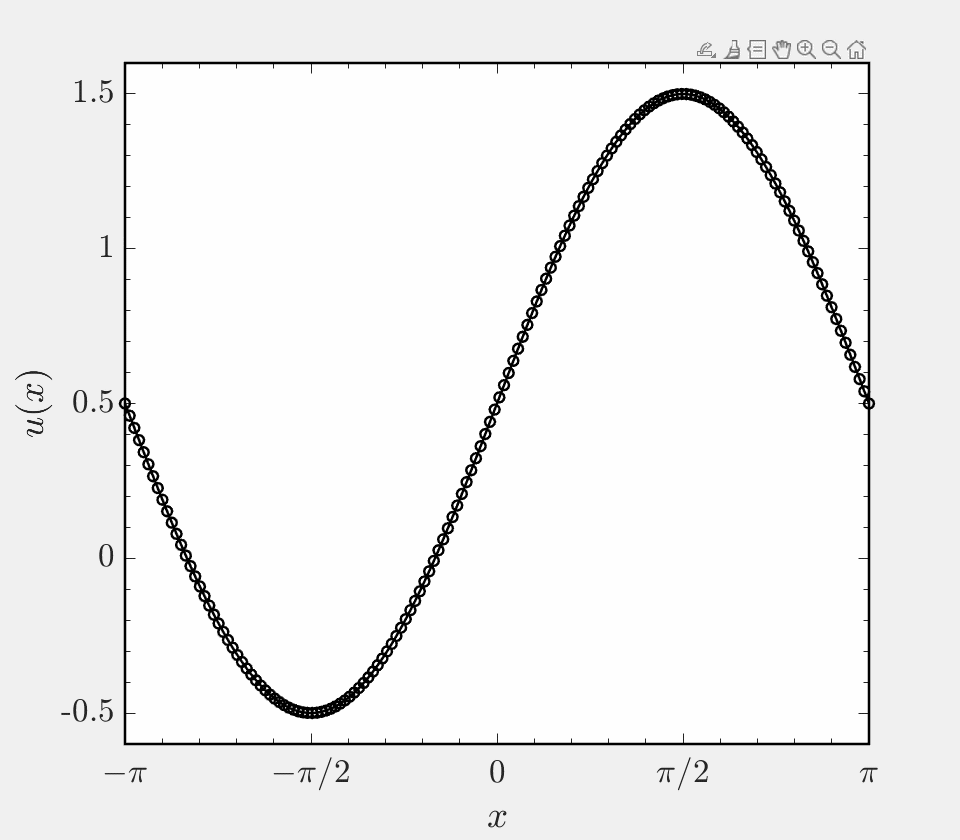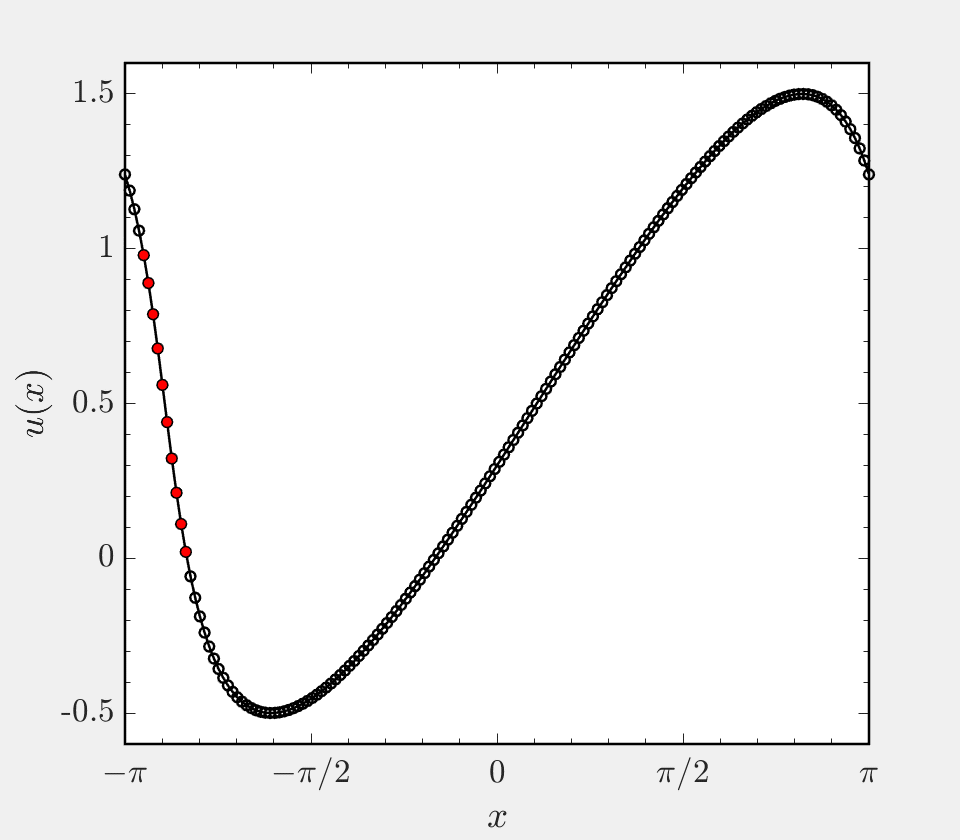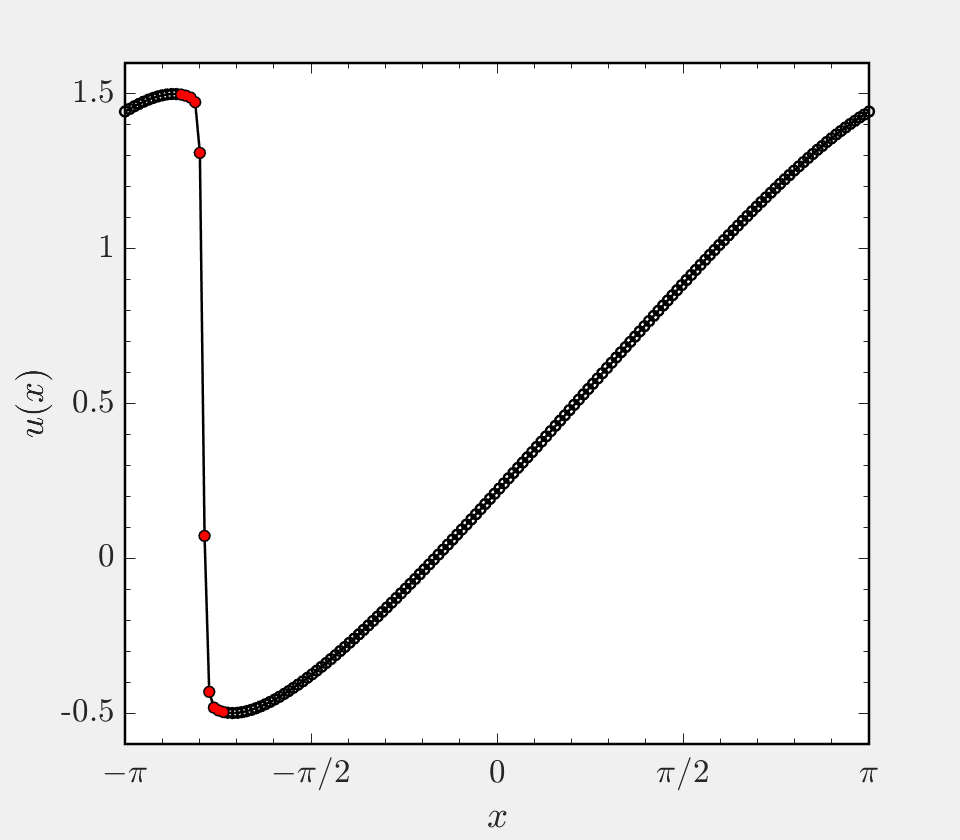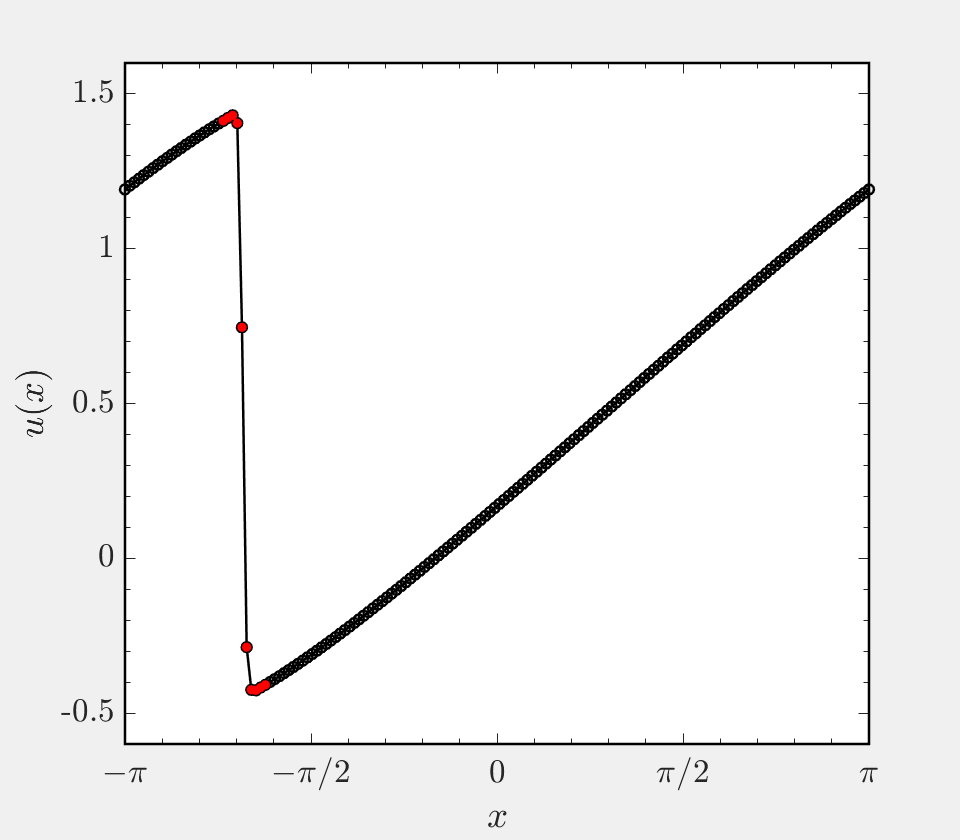
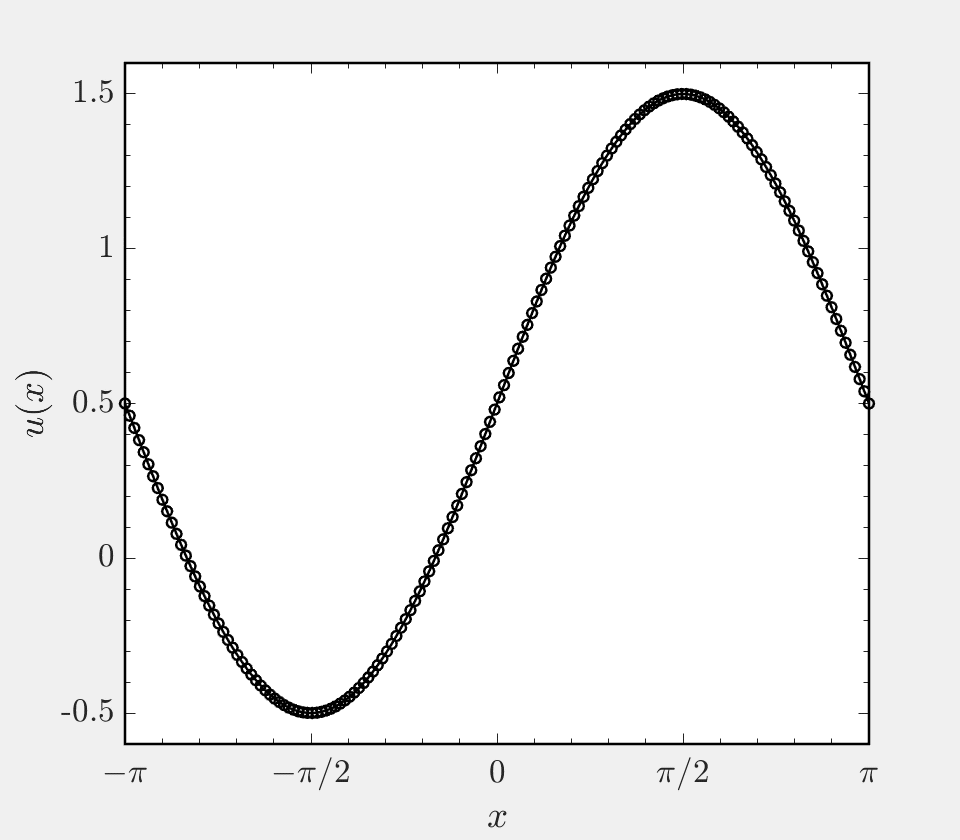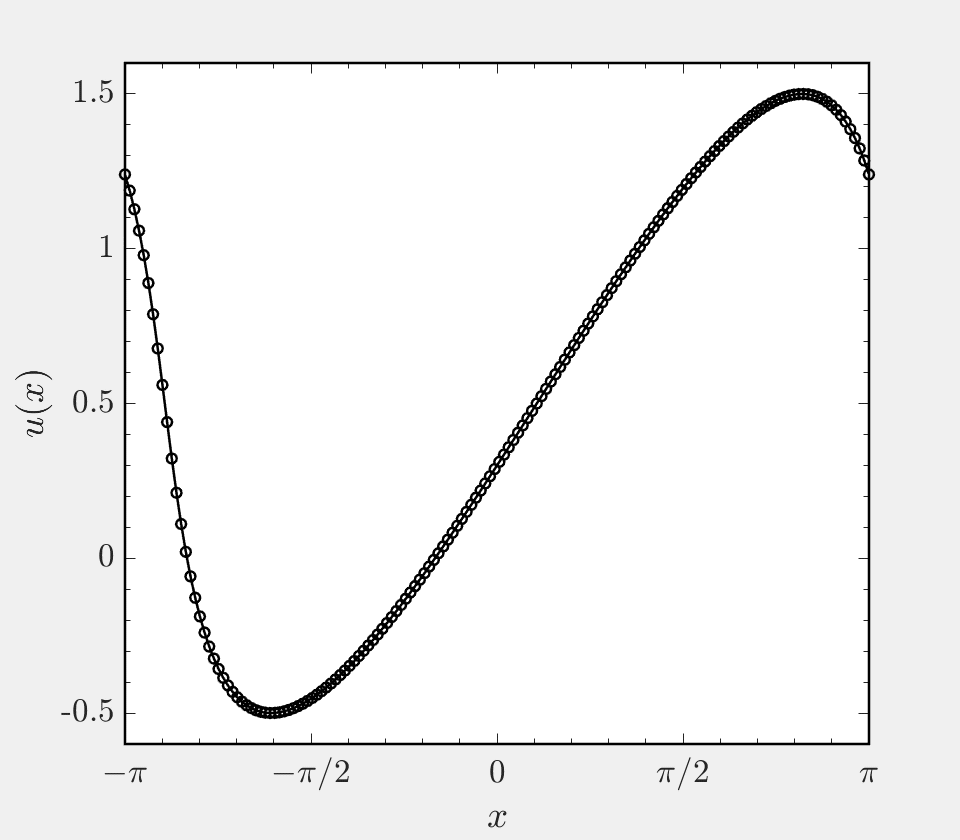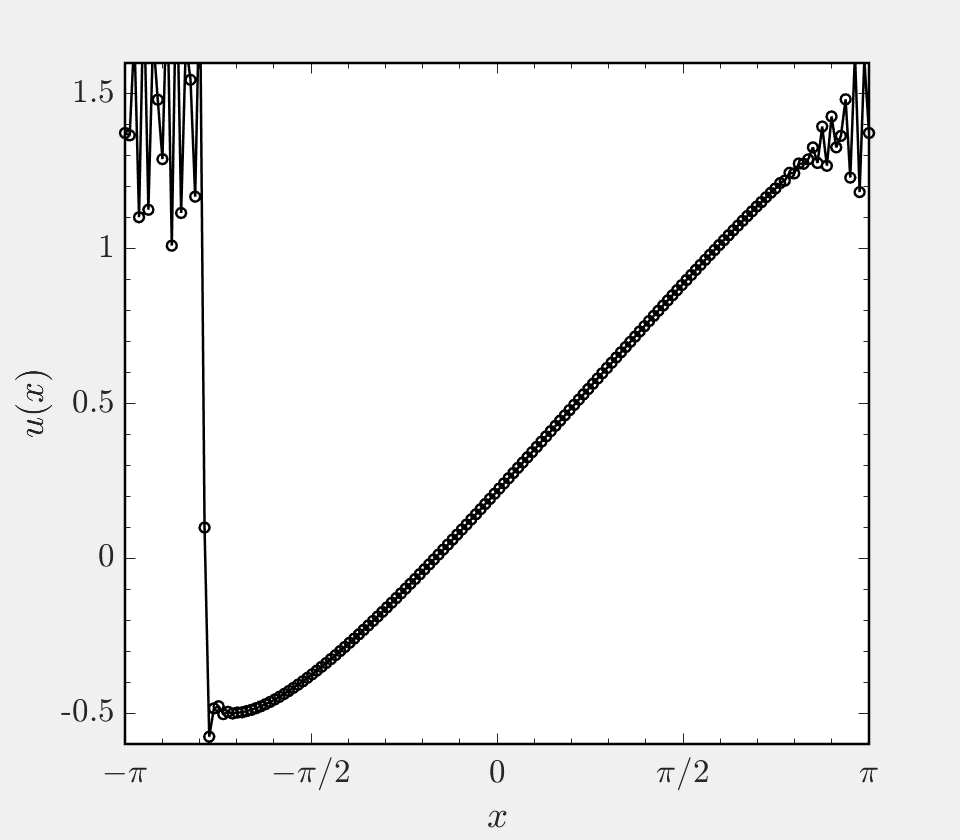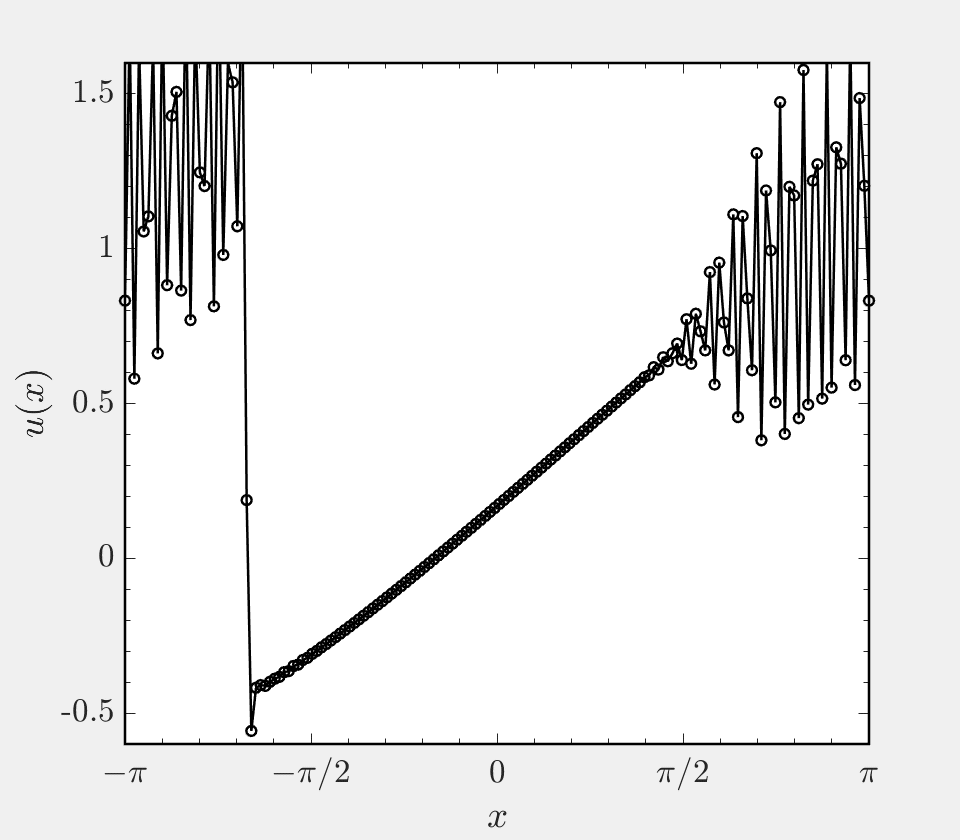
This project focuses on the implementation of a hybrid finite difference scheme for hyperbolic systems. In many simulations, the system being considered has both regions of smooth solution and regions of discontinuous solution. A prime example of this is the case of a shock wave interacting with turbulence, where near the shock gradients are large and (infinitely) steep and away from the shock the flow varies smoothly in space. In such settings, it is beneficial to use a non-dissipative central differencing scheme in smooth regions and a shock capturing scheme in shocked regions. To enable accurate simulation, these two classes of scheme must be coupled to one another or ‘hybridized’. This code base presents a hybrid finite difference approach to solving Burgers’ equation on a periodic domain, and allows one to use a central scheme of order 2, 4, 6, or 8 in smooth regions and the WENO5 scheme of Jhang and Shu in shocked regions.